Your cart is currently empty!
Shipping Update: Our shipping policies have changed! Some states have restrictions on certain products. Click here to learn more!
April 4th, 2019
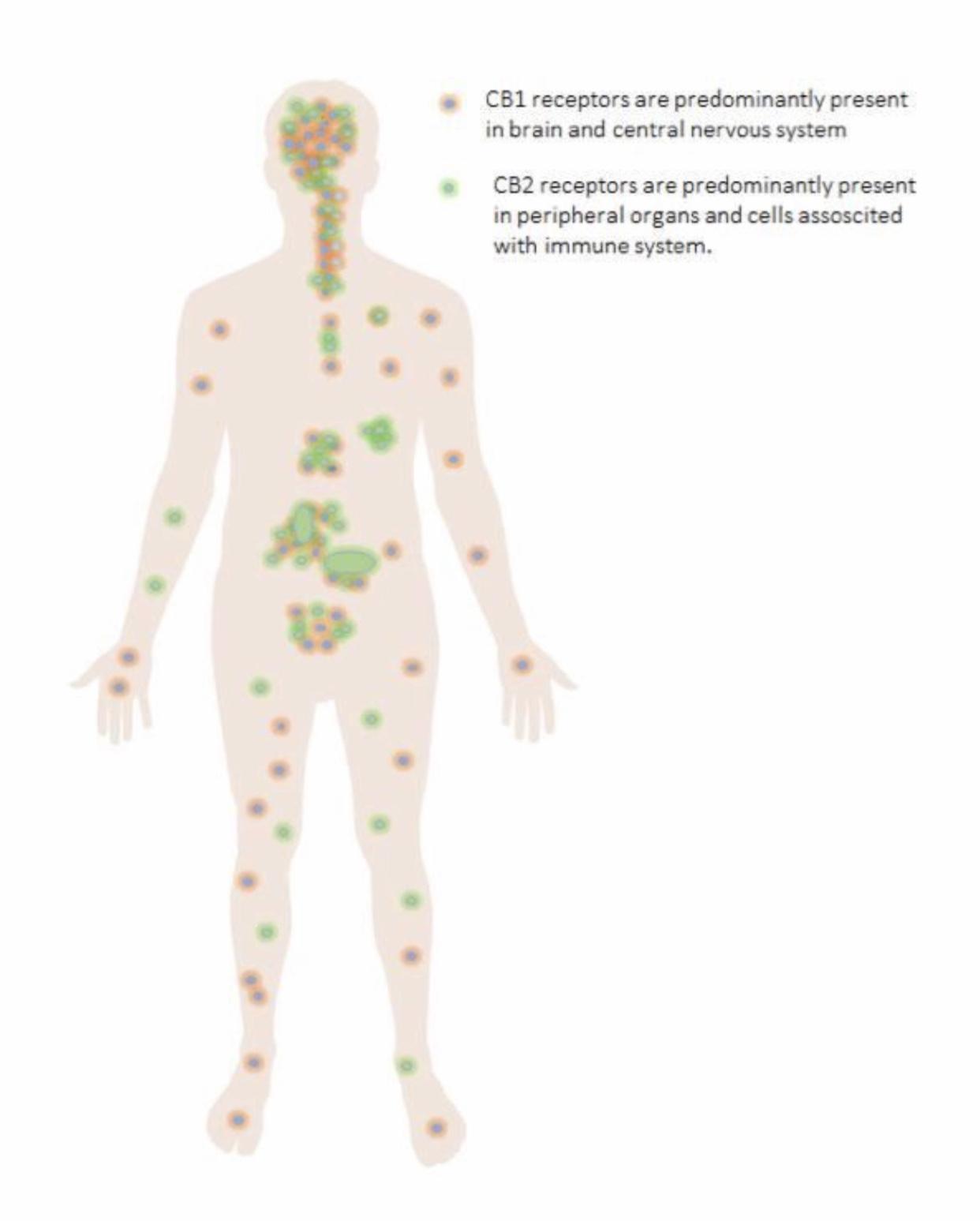
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex signaling network within the bodies of all mammals that utilizes different receptors, regulatory enzymes, and specialized components such as cannabinoids, to control, influence, and regulate various bodily processes. The body produces its own cannabinoids called endogenous cannabinoids or endocannabinoids. The first known endocannabinoid discovered is Anandamide, which is named after the Sanskrit word ananda meaning “bliss or supreme joy”. It was discovered after cloning an ECS receptor site, CB1, which by existing indicated that there was a substance within our bodies that attached to that receptor site. A few years later the cloning of another receptor site, CB2, led to the discovery of 2-AG (2-arachidonoyl-glycerol), another endocannabinoid. The cannabinoid receptor sites are located on the cell surfaces throughout the human body. CB1 receptors are concentrated in the central nervous system and the brain. CB2 receptors are concentrated in the peripheral organs and the immune system.




How would you like to shop?